شرح تقنية جودة الخدمة Quality of service ومشاكل وتطبيقات QOS
جودة الخدمة (Quality of Service – QoS): المفهوم والأهمية
تمثل جودة الخدمة (QoS) أحد أبرز المفاهيم المحورية في عالم الشبكات الحديثة والبنية التحتية للاتصالات، حيث غدت هذه التقنية مطلباً أساسياً في ظل تزايد استخدام التطبيقات ذات المتطلبات الزمنية الحرجة، وارتفاع سقف توقعات المستخدمين من حيث السرعة والثبات والموثوقية. يعتمد نجاح الشبكات في توفير تجربة استخدام مُرضية على قدرة البنية التحتية على تخصيص الموارد وضمان وصول البيانات بالسرعة المناسبة والجودة المطلوبة، مع الحد من الانقطاعات والتشوهات والاختناقات. ومع انتشار خدمات البث المرئي والاتصالات الصوتية عبر بروتوكول الإنترنت (VoIP) والخدمات السحابية والألعاب الإلكترونية التفاعلية، لم يعد بالإمكان الاعتماد على نموذج الخدمة الافتراضي “أفضل جهد” (Best-Effort Service) وحده لتلبية المتطلبات المتنامية. لهذا السبب، نشأت تقنيات QoS لتقدم إطاراً متكاملاً لإدارة حركة البيانات والتحكم في سعات القنوات وتقليل التأخير والارتجاف (Jitter) وفقدان الحزم.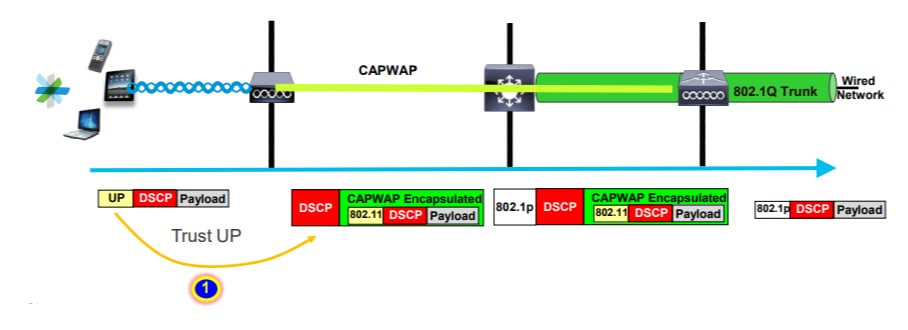
يتناول هذا المقال شرحاً تفصيلياً وشاملاً لمفهوم جودة الخدمة، بدءاً من الأسس النظرية ومروراً بالمعايير المؤثرة في QoS وآليات تنفيذها، ووصولاً إلى التحديات العملية التي تواجه تطبيقها في البنى التحتية المعاصرة. كما يستعرض المقال تطبيقات QoS في مجالات مختلفة كالصوت والفيديو والبث المباشر والألعاب التفاعلية، إضافة إلى نماذج البروتوكولات والتقنيات المستخدمة لتحسين الأداء وتحقيق مستويات جودة عالية ومستقرة. وأخيراً، يناقش المقال المشاكل والتحديات التي تظهر عند محاولة تطبيق جودة الخدمة على نطاق واسع، والاتجاهات البحثية المستقبلية لتطوير هذه التقنية.
أهمية QoS في الشبكات الحديثة
شهدت البنى التحتية للشبكات خلال العقود الماضية تحولات جذرية رافقها تنوع كبير في أنواع حركة البيانات ومتطلباتها. فبينما كانت الشبكات في الماضي تقتصر على نقل البيانات النصية والبريد الإلكتروني، أصبحت اليوم تتحمل أعباء هائلة من الفيديو فائق الدقة، والاتصالات الصوتية بالزمن الحقيقي، والمؤتمرات المرئية عالية الجودة، والتطبيقات السحابية الضخمة. هذا التحول لم يكن ليحدث لولا تطوير آليات وتقنيات متقدمة للتحكم في حركة البيانات وضمان مستويات أداء مستقرة.
تأتي QoS كاستجابة طبيعية لهذه الحاجة. فهي تقدم إطاراً يسمح للشبكات بتمييز أنواع حركة المرور المختلفة وفقاً لأولوياتها، ومن ثم تخصيص الموارد لها بما يتوافق مع احتياجاتها الخاصة. فعلى سبيل المثال، تتطلب حزم الصوت والفيديو زمناً انتقالياً منخفضاً وثباتاً في معدل الإرسال، بينما قد تتحمل تطبيقات نقل الملفات بعض التأخير دون التأثير الكبير على تجربة المستخدم. كما تسمح QoS بمكافحة الازدحام وتنظيم المرور داخل الشبكات المزدحمة، مما يسهم في الحد من فقدان الحزم وتحسين تجربة المستخدم النهائي.
مفهوم جودة الخدمة: التعريف والمعايير الأساسية
التعريف
تعرف جودة الخدمة على أنها مجموعة من التقنيات والآليات التي تمكن الشبكات من توفير مستويات مختلفة من أداء نقل البيانات بناءً على متطلبات التطبيقات والمستخدمين. تهدف هذه التقنيات إلى تحسين عناصر الأداء الرئيسية مثل زمن الوصول (Latency)، الارتجاف (Jitter)، معدل فقدان الحزم (Packet Loss)، وعرض الحزمة (Bandwidth)، وتخصيص الموارد بصورة ديناميكية لضمان تحقيق أهداف الأداء المنشودة.
المعايير الأساسية في QoS
يعتمد تقييم جودة الخدمة على مجموعة من المعايير والمؤشرات التي تستخدم لقياس مدى جودة النقل الشبكي:
- زمن الوصول (Latency): يقيس الوقت الذي تستغرقه حزمة البيانات للانتقال من المصدر إلى الوجهة. يعتبر زمن الوصول المنخفض ضرورياً لتطبيقات الزمن الحقيقي مثل الصوت والفيديو التفاعلي.
- الارتجاف (Jitter): يشير إلى التباين في زمن الوصول بين الحزم المتتالية. ارتفاع الارتجاف يؤدي إلى تذبذب ملحوظ في جودة الصوت والفيديو ويؤثر سلباً على تجربة المستخدم.
- فقدان الحزم (Packet Loss): يدل على عدد الحزم التي تفقد أثناء النقل. فقدان الحزم بنسب عالية يؤدي إلى تشوهات في الصوت والفيديو، وصعوبة في الحفاظ على الاتصال الموثوق.
- عرض الحزمة (Bandwidth): يمثل معدل نقل البيانات الأقصى الممكن على طول المسار الشبكي. كلما زاد عرض الحزمة المتاح لتدفق معين، تحسّنت احتمالات الحصول على أداء أفضل.
- نسبة الخطأ (Bit Error Rate – BER): تشير إلى نسبة الأخطاء في البتات المنقولة. يمكن لهذه الأخطاء أن تؤثر على جودة البيانات، خاصة في التطبيقات الحرجة.
مشاكل QoS والتحديات التقنية
على الرغم من الفوائد العديدة التي تقدمها تقنيات جودة الخدمة، إلا أنها تصطدم بعدد من التحديات والمشكلات التي تعرقل استغلالها على نطاق واسع، من أبرزها:
- التعقيد في إدارة الموارد: يتطلب تطبيق QoS آليات معقدة لإدارة الموارد وتخصيصها على نحو ديناميكي. هذا الأمر يزيد من تعقيد بروتوكولات التوجيه وإدارة الشبكة، وقد يتطلب استثماراً كبيراً في البنية التحتية والأجهزة.
- التوسع وقابلية التدرج (Scalability): مع نمو الشبكات واتساعها، يصبح من الصعب الحفاظ على مستويات QoS ثابتة. يطرح الانتشار الواسع لعدد هائل من الأجهزة والتطبيقات عبئاً إضافياً على إدارة QoS.
- التوافقية مع البنى الموجودة: قد تتطلب QoS تعديلات جذرية في البنية الأساسية لبعض الشبكات القديمة، الأمر الذي قد لا يكون عملياً أو مجدياً من حيث التكلفة.
- الأمان والخصوصية: في بعض الأحيان، قد تتداخل آليات QoS مع بروتوكولات التشفير أو تتسبب في كشف بعض السمات المرورية، مما يخلق تحديات إضافية في تأمين البيانات وحماية الخصوصية.
- الكلفة المرتفعة: تطبيق QoS على نحو شامل قد يتطلب استثمارات في معدات دعم متقدمة، وأجهزة توجيه ومفاتيح (Switches) ذات قدرات عالية، وفرق تقنية مؤهلة.
البروتوكولات والآليات الداعمة لجودة الخدمة
النموذج التكاملي (Integrated Services – IntServ)
يعد IntServ واحداً من الأساليب المبكرة لتطبيق جودة الخدمة في شبكات IP. يعتمد على حجز الموارد مسبقاً لكل تدفق (Flow) قبل البدء في الإرسال. يستعين IntServ ببروتوكول حجز الموارد (Resource Reservation Protocol – RSVP) لضمان الحصول على الموارد اللازمة (عرض حزمة، مخازن) لتلبية متطلبات التطبيقات.
على الرغم من دقة هذا النموذج في توفير مستويات عالية من QoS، إلا أن قابليته للتوسع محدودة، إذ يتعين على كل مسار شبكي في الشبكة التعامل مع العديد من طلبات الحجز، مما يؤدي إلى تعقيد إداري وضغط على أجهزة التوجيه.
النموذج التفاضلي (Differentiated Services – DiffServ)
جاء نموذج DiffServ كبديل أكثر قابلية للتوسع، يعتمد على تصنيف حركة البيانات إلى فئات مختلفة، وتطبيق سياسات معالجة محددة لكل فئة. بدلاً من حجز الموارد لكل تدفق، يقوم DiffServ بوضع علامات على الحزم (Marking) في أطراف الشبكة، ثم يتم تنفيذ سياسات محددة وفقاً لهذه العلامات، مثل تخصيص نسب من عرض الحزمة، والتحكم في طوابير الانتظار، وإدارة الازدحام.
يتميز DiffServ بسهولة التنفيذ وبساطة الإدارة النسبية، ويستخدم على نطاق واسع في الشبكات الواسعة (WAN) ومزودي خدمات الإنترنت. لكنه يفتقر إلى الضمانات الصارمة التي يقدمها IntServ، إذ يقدم QoS أقرب للطابع الإحصائي منه إلى الضمانات القاطعة.
التبديل متعدد البروتوكولات باستخدام المؤشرات اللاصقة (MPLS)
تعتبر تقنية التبديل متعدد البروتوكولات (MPLS) حلاً فعالاً لتقديم QoS في الشبكات الأساسية. تعتمد MPLS على استخدام تسميات (Labels) لتوجيه الحزم عبر الشبكة، مما يتيح إمكانية التحكم الدقيق في تدفقات البيانات. يمكن تطبيق سياسات QoS على المسارات المسماة (LSP – Label Switched Paths) وتوفير مستويات مختلفة من الخدمة لكل تدفق. تساعد MPLS في تحقيق زمن وصول أقل وتوجيه متقدم، إلى جانب تحسين استخدام الموارد.
التحكم في الازدحام وإدارة قوائم الانتظار
تشكل آليات إدارة قوائم الانتظار (Queue Management) والتحكم في الازدحام عنصراً مهماً في QoS. تشمل هذه الآليات:
- الطوابير ذات الأولوية (Priority Queuing – PQ): تمنح الحزم ذات الأولوية العليا حق المعالجة أولاً، مما يضمن زمن وصول منخفضاً لتطبيقات الزمن الحقيقي.
- الطوابير العادلة المرجحة (Weighted Fair Queuing – WFQ): تخصص عرض الحزمة بشكل عادل بين التدفقات، مع إعطاء وزن أكبر للتدفقات ذات الأهمية.
- التحكم العشوائي المبكر في الازدحام (Random Early Detection – RED): آلية للحد من الازدحام عبر إسقاط بعض الحزم عشوائياً قبل امتلاء الطابور.
- الطوابير العادلة المرجحة باستخدام الفئات (Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing – CBWFQ): توزع عرض الحزمة بين الفئات المختلفة وفقاً للأوزان المحددة لكل فئة.
تطبيقات QoS في مجالات مختلفة
الصوت عبر بروتوكول الإنترنت (VoIP)
يعتبر VoIP من أبرز التطبيقات التي تعتمد على QoS، حيث تتطلب محادثات الصوت جودة عالية وزمن وصول منخفض للغاية. يمكن لتقنيات QoS تخصيص عرض حزمة كافٍ لحركة الصوت، وضمان عدم انقطاع المكالمات أو تشوهها. يقوم هذا على الحد من التأخير والارتجاف وتحجيم فقدان الحزم. بدون QoS، قد تؤدي حزمات البيانات الأخرى إلى تأخير الصوت، مما يتسبب في تجربة استماع غير مقبولة.
الفيديو التفاعلي والمؤتمرات المرئية
تتطلب خدمات البث المباشر للمؤتمرات المرئية والأحداث الرياضية والفيديو حسب الطلب (VoD) تقليل التأخير والارتجاف وضمان معدل بث ثابت. توفر QoS إمكانية تخصيص مسارات مفضلة لتدفقات الفيديو ذات الأولوية وتطبيق سياسات خاصة لضمان عدم تعرّض هذه التدفقات للازدحام الحاد. وبذلك، يحصل المشاهدون على جودة صورة عالية وخالية من الانقطاع والتشوهات.
الألعاب الإلكترونية عبر الإنترنت
تُعد الألعاب التفاعلية عبر الإنترنت من أكثر التطبيقات حساسية للزمن. يتوقف أداء اللعبة وتجربة المستخدم على سرعة استجابة الخادم وحصول اللاعب على المعلومات اللازمة من الشبكة دون تأخير ملحوظ. تتيح QoS آليات للموازنة بين حركة الألعاب ذات الأولوية العالية وحركة التطبيقات الأخرى في الشبكة، لضمان زمن وصول منخفض جداً.
التطبيقات الصناعية والطبية
في مجال التصنيع الذكي (Industry 4.0) والروبوتات والعمليات التحكّمية، تحتاج الأنظمة إلى ضمانات زمنية صارمة للتواصل بين أجهزة الاستشعار والمتحكمات. كما يحتاج مجال الطب عن بعد (Telemedicine) وجراحات الروبوت عن بعد إلى زمن وصول منخفض للغاية ونسبة فقدان حزم تكاد تكون معدومة. هنا تكمن أهمية QoS في توفير منصة اتصالات موثوقة وآمنة وصارمة من حيث المواعيد الزمنية.
تطبيقات إنترنت الأشياء (IoT) والشبكات ذات النطاق الضيق
يعمل إنترنت الأشياء على ربط مليارات الأجهزة، بدءاً من المستشعرات الصناعية وصولاً إلى الأدوات المنزلية الذكية. تختلف متطلبات QoS في IoT حسب طبيعة التطبيق، فبعض التطبيقات تحتاج إلى موثوقية عالية وتأخير منخفض، في حين أن البعض الآخر يمكنه العمل بنظام “أفضل جهد”. تساعد QoS في تخصيص الموارد للتطبيقات الحرجة مثل أنظمة المراقبة الأمنية وأجهزة مراقبة صحة المرضى.
دور QoS في الشبكات المستقبلية
الشبكات المعرفة بالبرمجيات (SDN) والافتراضية
ساهمت شبكات التحكم بالبرمجيات (SDN) وتقنيات افتراضية وظائف الشبكات (NFV) في تسهيل إدارة QoS. فمن خلال فصل طبقة التحكم عن طبقة التوجيه، يمكن للمسؤولين تحسين تخصيص الموارد ديناميكياً وتطبيق سياسات QoS بشكل مرن. تتيح هذه البنية المرونة في إدارة الموارد وفقاً للطلب، مما يحسن قابلية التدرج ويساعد على تلبية متطلبات التطبيقات المتغيرة.
الجيل الخامس (5G) والشبكات الخلوية المتقدمة
تعتمد شبكات الجيل الخامس على توفير فئات خدمة متعددة ذات متطلبات مختلفة من حيث زمن الوصول ومعدل البيانات. توفر QoS إطاراً مهماً لضمان أداء خدمات النطاق العريض المتنقل فائقة السرعة، واتصالات الآلة، وإنترنت الأشياء الصناعية. تعمل 5G على تقسيم الشبكة إلى شرائح (Network Slicing) بحيث يمكن تلبية متطلبات كل شريحة باستخدام سياسات QoS مخصصة.
الذكاء الاصطناعي والتعلم الآلي في إدارة QoS
مع ازدياد تعقيد الشبكات وتنوع التطبيقات، يصبح من الصعب إدارة QoS يدوياً. هنا يأتي دور الذكاء الاصطناعي والتعلم الآلي لتوفير تحليلات ذكية لحركة المرور، والتنبؤ باحتياجات الموارد، وضبط السياسات تلقائياً. يمكن لهذه التقنيات أن تتعلم من أنماط حركة البيانات وتحسن تخصيص الموارد بمرور الوقت، مما يزيد من كفاءة QoS واستقرارها.
الجدول التوضيحي لبعض معايير QoS وتأثيرها على التطبيقات
| المعيار | الوصف | التطبيقات الحساسة | الأثر عند عدم التوافر |
|---|---|---|---|
| زمن الوصول (Latency) | الوقت المستغرق لوصول الحزمة من المصدر إلى الوجهة | المكالمات الصوتية، الألعاب التفاعلية | تأخير في الاستجابة، تشوه الصوت، صعوبة التحكم الفوري |
| الارتجاف (Jitter) | التغير في زمن الوصول بين الحزم المتعاقبة | الفيديو المباشر، مؤتمرات الفيديو | تقطع في الصورة والصوت، جودة عرض متذبذبة |
| فقدان الحزم (Packet Loss) | النسبة المئوية للحزم المفقودة أثناء النقل | الصوت والفيديو، تحكم العمليات الصناعية | انقطاع في الصوت، فقدان إطارات فيديو، تعطل إجراءات التحكم |
| عرض الحزمة (Bandwidth) | معدل نقل البيانات الأقصى عبر القناة | البث عالي الدقة، نقل الملفات الكبيرة | تخفيض جودة الفيديو، بطء تنزيل الملفات |
استراتيجيات التصميم والتنفيذ لـ QoS
تنفيذ QoS في الشبكة ليس عملية بسيطة، بل يتطلب تبني استراتيجيات دقيقة ومرنة. ومن بين هذه الاستراتيجيات:
- تصنيف حركة البيانات (Traffic Classification): الخطوة الأولى هي تحديد أنواع حركة المرور وتطبيق معايير QoS عليها. يتم ذلك عبر تحليلات الطبقة السابعة (Layer 7) للتعرف على التطبيقات، أو العلامات (Tags) التي يضعها البروتوكول.
- وضع العلامات (Marking): بعد التصنيف، توضع علامة على الحزم لتدل على فئتها أو أولويتها. تستخدم حقول محددة في ترويسات الحزم (مثل DSCP في نموذج DiffServ) للتعبير عن هذه الأولوية.
- تشكيل حركة المرور (Traffic Shaping) وتحديد المعدل (Policing): تستخدم هذه التقنيات للتحكم في معدل البيانات المسموح بها للتدفقات المختلفة. يساعد تشكيل حركة المرور في ضمان عدم تجاوز التطبيقات لمعدل الإرسال المتفق عليه.
- إدارة قوائم الانتظار (Queue Management): تطبيق خوارزميات انتقاء الحزم وتنظيمها في الطوابير، مثل WFQ أو PQ، لضمان أولوية مناسبة للتطبيقات الحرجة.
- مراقبة الأداء (Monitoring): مراقبة مستمرة للأداء والاطلاع على مؤشرات QoS، مثل زمن الوصول ونسبة فقدان الحزم، وضبط السياسات حسب الحاجة.
الأبعاد التنظيمية والقانونية لجودة الخدمة
لا تقتصر QoS على الجانب التقني فقط، بل تمتد لتشمل أبعاداً تنظيمية وقانونية. فقد تفرض بعض الدول تشريعات ومعايير محددة لضمان توفير حد أدنى من الجودة في خدمات الاتصالات المقدمة للمواطنين. كما قد تضع هيئات تنظيم الاتصالات متطلبات على مزودي الخدمات لضمان عدم تمييز حركة المرور على أساس المحتوى أو المصدر، مع الحفاظ في الوقت ذاته على جودة الخدمة للتطبيقات الحرجة.
من ناحية أخرى، قد تثير آليات QoS مسائل تتعلق بالحيادية الشبكية (Net Neutrality)، حيث قد يراها البعض وسيلة لتفضيل حركة مرور على أخرى. لذلك، فإن ضبط QoS يتطلب موازنة دقيقة بين احتياجات التطبيقات والمستخدمين وبين مبادئ العدالة وعدم التمييز بين البيانات.
التكامل بين QoS والأمان
بالرغم من أن QoS تركز على الأداء الزمني والكمي، إلا أن الجانب الأمني لا يقل أهمية. قد تحاول بعض الهجمات استغلال سياسات QoS لتحقيق مكاسب أو إحداث أضرار، مثل استخدام حركة مرور ضارة عالية الأولوية لتعطيل خدمات أخرى. هنا تبرز الحاجة لتكامل QoS مع آليات أمن الشبكات، مثل التحليل السلوكي لحركة المرور واستخدام أنظمة كشف التسلل (Intrusion Detection Systems – IDS) للتمييز بين الحركة المشروعة وغير المشروعة.
مشاكل QoS في بيئات متعددة البروتوكولات
مع تنوع البروتوكولات والمعايير المستخدمة في الشبكات المختلفة، قد تنشأ تحديات في تطبيق QoS بشكل متجانس. فعلى سبيل المثال، يختلف مفهوم QoS في شبكات MPLS عنه في شبكات Wi-Fi، وقد لا تتوفر نفس حقول العلامات أو الآليات. إضافة إلى ذلك، يصعب تحقيق QoS في بيئات الإنترنت العامة، حيث لا تستطيع جهة واحدة التحكم في جميع مراحل نقل البيانات. هذا يتطلب اتفاقيات بين مزودي الخدمة والتعاون عبر الحدود لتوفير QoS من طرف إلى طرف.
الحلول المستندة إلى التخزين المؤقت والتكييف الديناميكي
قد تلجأ بعض التطبيقات والأساليب لتحسين QoS من خلال زيادة الاعتماد على آليات تخزين مؤقت (Buffering) لتحسين تجربة المشاهدة في البث المرئي، إذ يتم استباق تشغيل المحتوى عن طريق تخزين جزء منه محلياً قبل عرضه. كما تعتمد استراتيجيات أخرى على الضبط الديناميكي لمعدل الإرسال وفقاً لجودة الاتصال الحالية، فمثلاً يضبط تطبيق الفيديو معدل البث وجودته وفقاً لحالة الشبكة آنياً لتقليل الارتجاف والتقطعات.
التكامل مع تقنيات التوجيه المتقدم
تعتمد QoS على وجود مسارات شبكة مناسبة توفر خصائص زمنية مناسبة. يساعد التوجيه المتقدم، مثل التوجيه باستناد الجودة (Quality-Aware Routing) واختيار المسارات ديناميكياً حسب مؤشرات الأداء، على تحسين مستويات QoS. يتطلب ذلك توافر معلومات آنية حول حالة الشبكة، وإمكانية تغيير المسارات في حال حدوث ازدحام أو خلل.
QoS في البيئات الافتراضية والسحابية
تحولت الكثير من الخدمات إلى السحابة، حيث البنية التحتية الافتراضية. في هذه الحالة، يصبح تطبيق QoS أكثر تعقيداً، إذ قد يتعين على مزود الخدمة السحابية ضمان موارد عرض حزمة وحساب وتخزين متسقة مع سياسات QoS. يتم اللجوء إلى تقنيات مثل ترتيب الموارد الافتراضية (Virtual Resource Allocation) والتحكم الديناميكي في عرض الحزمة الافتراضية لمجاراة المتطلبات المتغيرة للتطبيقات.
تقييم الأداء واختبار QoS
لا يمكن الاعتماد فقط على الضبط النظري لـ QoS دون التحقق من النتائج الفعلية. يتطلب الأمر إجراء اختبارات دورية لقياس الأداء والتحقق من تحقيق الأهداف المنشودة. يمكن استخدام أدوات قياس زمن الوصول وفقدان الحزم وجودة الصوت والفيديو، وتحليل سجلات حركة المرور، ورصد نسبة العملاء الراضين (Quality of Experience – QoE) كمؤشر نهائي على نجاح سياسات QoS.
الاعتبارات الاقتصادية والاستثمارية
يجب على الشركات ومزودي الخدمات الموازنة بين كلفة تنفيذ QoS والفوائد المحتملة. قد يتطلب التحسين الشامل في QoS استثمارات كبيرة في الأجهزة والبرمجيات والكوادر المؤهلة. في المقابل، تحقق QoS قيمة اقتصادية ملموسة عن طريق تحسين تجربة المستخدم، والحد من الشكاوى، وزيادة رضا العملاء، وجذب شرائح جديدة من المستخدمين الذين يعتمدون على تطبيقات ذات متطلبات زمنية حرجة.
مدى رضى المستخدم النهائي: QoE مقابل QoS
على الرغم من أن QoS تقدم مقاييس تقنية لقياس جودة الشبكة (زمن وصول، ارتجاف، فقدان حزم)، فإن ما يهم المستخدم النهائي هو جودة التجربة (QoE)، والتي تتأثر بعوامل تتجاوز المؤشرات الفنية. فقد تجد تطبيقات تستخدم تقنيات تصحيح الأخطاء وتجميع الحزم لتحسين الجودة الظاهرة للمستخدم حتى لو كانت ظروف الشبكة دون المستوى الأمثل. لذا، لا يمكن الاعتماد على QoS وحدها لضمان الرضى، بل يجب النظر أيضاً في تقنيات تحسين QoE.
مستقبل QoS: نحو شبكات أكثر ذكاءً وتكيفاً
مع تطور التقنيات وازدياد تعقيد الشبكات، يتوقع أن تصبح QoS أكثر ذكاءً وقدرة على التكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة. ستلعب الذكاء الاصطناعي والتحليلات التنبؤية دوراً محورياً في توقع الأحمال المرورية وضبط السياسات استباقياً. كما أن تطور معايير الاتصالات اللاسلكية السريعة (مثل Wi-Fi 7) وزيادة انتشار الألياف الضوئية سيوفر بنية تحتية داعمة لـ QoS متقدمة.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، قد نشهد ظهور بروتوكولات أكثر مرونة وواجهات برمجية تتيح للمطورين التحكم في QoS بشكل مباشر. هذا سيسمح للتطبيقات الحرجة بالتفاوض مع الشبكة بشأن جودة الخدمة المطلوبة، وتحسين كيفية تخصيص الموارد حسب الحاجة الفعلية.
دراسات حالة واقعية لتطبيق QoS
من أهم طرق فهم QoS بشكل أفضل النظر في دراسات حالة من الواقع. على سبيل المثال، قد نجد مزود خدمة إنترنت يطبق DiffServ في شبكة النطاق العريض الخاصة به لضمان جودة بث الفيديو عالي الدقة. هناك أيضاً حالات استخدام في قطاع الصحة، حيث يتم تشغيل أنظمة مراقبة المرضى عن بعد عبر شبكات مدعومة بـ QoS لتأمين زمن وصول منخفض وموثوقية عالية.
دراسة حالة أخرى قد تشمل شركة اتصالات دولية تستخدم MPLS لتوفير مسارات شبكة ذات زمن وصول منخفض بين مراكز البيانات المنتشرة عالمياً، مما يضمن سرعات عالية لتطبيقات التخزين السحابي وتزامن البيانات.
كيفية تلبية متطلبات QoS للتطبيقات الناشئة
مع ظهور تطبيقات ناشئة مثل الواقع الافتراضي (VR) والمعزز (AR)، والقيادة الذاتية للمركبات، والطائرات دون طيار المتصلة، ستزداد الحاجة إلى QoS صارمة. في الواقع المعزز مثلاً، يتطلب الأمر زمن وصول منخفض جداً للتفاعل مع العالم الحقيقي في الزمن الفعلي. ولهذا، يجب تطوير سياسات QoS تلبي هذه الاحتياجات المتطرفة، وإيجاد حلول تقنية قادرة على تقليل زمن الوصول إلى بضعة أجزاء من الألف من الثانية.
إشراك المستخدم النهائي وصناع القرار
من المهم أن يفهم المستخدمون وصناع القرار أهمية QoS ودورها. فالتوعية حول كيفية عمل QoS وفوائدها يمكن أن تساعد في تخفيف التوقعات غير الواقعية. على سبيل المثال، قد يدرك المستخدم أنه على الرغم من بعض التأخير البسيط في تحميل الفيديو، إلا أن جودة الصورة والصوت ستظل مرتفعة بفضل سياسات QoS المطبقة. أما صناع القرار والمستثمرون، فيمكنهم تقدير العوائد الاقتصادية والاجتماعية لتنفيذ QoS.
خلاصة
باتت QoS حجر الزاوية في تصميم وإدارة الشبكات الحديثة، إذ توفر إطاراً شاملاً للتحكم في حركة المرور وضمان مستويات أداء تتناسب مع متطلبات التطبيقات المختلفة. على الرغم من التحديات التقنية والتنظيمية والاقتصادية، فإن الفوائد التي تقدمها QoS على صعيد تحسين تجربة المستخدم وتعزيز الموثوقية والاستفادة القصوى من الموارد تجعلها من الركائز الأساسية في بنية الاتصالات المعاصرة. إن المستقبل ينبئ بمزيد من التكامل بين QoS والتقنيات الناشئة كالشبكات المعرفة بالبرمجيات، والحوسبة السحابية، وإنترنت الأشياء، مما سيسهم في بناء بيئة اتصالية أكثر مرونة وذكاءً.
المراجع والمصادر
- G. Almes, S. Kalidindi, and M. Zekauskas, “A one-way delay metric for IPPM,” RFC 2679, IETF, 1999.
- G. Armitage, “Quality of service in IP networks: foundational principles and recent standards,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 38, no. 5, 2000.
- J. Wroclawski, “The use of RSVP with IETF integrated services,” RFC 2210, IETF, 1997.
- S. Blake, D. Black, M. Carlson, E. Davies, Z. Wang, and W. Weiss, “An architecture for differentiated services,” RFC 2475, IETF, 1998.
- E. Rosen, A. Viswanathan, and R. Callon, “Multiprotocol label switching architecture,” RFC 3031, IETF, 2001.
- P. Chatzimisios, “QoS Mechanisms and Protocols,” in Next Generation Internet Networks, IEEE, 2011.
- M. G. Larsen, L. M. Kristensen, and K. S. Rønn, “Using SDN and NFV for dynamic QoS control,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 14, no. 4, 2017.
- R. Jain, “Quality of Experience: From User Perception to Network Design,” IEEE Internet Computing, vol. 21, no. 1, 2017.